INVESTMENT CASTING
Process

Step 1: Pattern manufacturing
With the help of injection press wax is injected into the die under required pressure, temperature to give a replica of the finished components. After injecting the pattern, clean-repair process is done for better finishing. Then we hand over pattern for inspection. Pattern dimensions are measured and visual inspection carried out

Step 2: Tree building
These wax models are glued onto a so-called wax tree with a casting funnel on top, into which steel is poured in a later stage off the process. After the wax models have been glued onto a wax tree, they are rinsed. Any possible contaminations on the surface are removed to ensure a successful attachment of the ceramic onto the wax tree.

Step 3: Building ceramic layers
After rinsing the wax tree, the tree is given a fireproof ceramic shell. This shell is constructed after repeatedly submerging the tree (up to 7 or 9 times) in a slurry and sprinkle it with ceramic sand. The ceramic layers are then hardened in a drying where they are exposed to air.

Step 4: Autoclave
After the layers have been formed and dried, the wax is melted out of the ceramic tree by using steam (125°C) in an autoclave. This is why it is called “lost wax casting”. The majority of the molten wax can be regenerated and is reusable at certain extent.
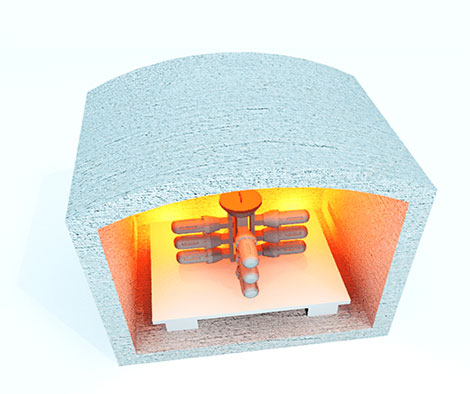
Step 5: Shell firing
The ceramic tree is then baked (stoked) at high temperatures of around 900°C – 1000°C and reaches its final strength through the sintering process. Any wax remains are burned out during this process & this prevent thermal shocks during the pouring process.

Step 6: Pouring
The desired steel alloy is melted in a furnace of 350kg and brought to cast temperatures. Then heated tree has been removed from shell firing oven and filled up with a steel alloy by use of ladle.
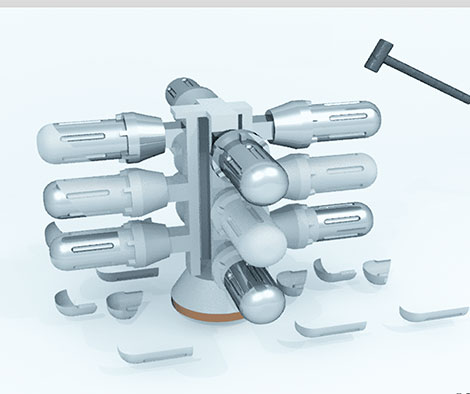
Step 7: Dismantle of tree
The trees are then removed from their ceramic shell, by using a hammer. This removes the majority of the ceramic. The next step is to cut the products from the trees by sawing or gauging or plasma cutting.

Step 8: Blasting, grinding and visual inspection
The Finishing Department removes the last pieces of ceramic by means of steel, sand and/or water blasting. The ingate which remained after the cutting process, is grinded /Machined from the casting. The Quality Department checks all products visually for possible casting failures. This check takes place according to a quality standard to ensure that all possible surface failures are corrected properly.

Step 9: Heat and surface treatment
The Finishing Department removes the last pieces of ceramic by means of steel, sand, and/or water blasting. The ingate which remained after the cutting process is grinded /Machined from the casting. The Quality Department checks all products visually for possible casting failures. This check takes place according to a quality standard to ensure that all possible surface failures are corrected properly.

Step 10: Final inspection
The final step in this process is another visual check and composing a measurement report and material analysis. After the final inspection, the products are ready for shipment to satisfied Cosmos customer.
